Laser Tattoo Removal
A recent poll in 2014 shows that the number of US adults who have a tattoo has increased to 45 million, or one in five (21%). This includes over half of all women over the age of 18. With the rise in tattoos, 'tattoo regret' has also been prevalent. In fact, research has shown that 20% of individuals with tattoos have 'tattoo regret', wishing that they had never gotten a tattoo. The amount of tattoo removal procedures models this trend, showing a 32% increase in 2011, and an even higher 43% increase in 2012.
The most common types of lasers for tattoo removal are:
- Q-switched Nd:YAG (Neodymium:Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser
- Q-switched Ruby laser
- Q-switched Alexandrite laser
- Picosecond Alexandrite laser
The choice of laser type is based on several factors, including the absorption spectrum of the target ink, the desired depth of penetration of the laser, the size of the ink particle, and the laser's wavelength and pulse duration.
How does laser tattoo removal work?
What makes tattoos permanent is that the size of the ink particles embedded in the skin are too large for the body's immune cells to clean up. Lasers work by producing very short pulses (several billionth of a second) of intense light energy that pass through the top layers of the skin to be selectively absorbed by the tattoo ink. Each laser treatment causes the tattoo pigment to fragment (break down) into progressively smaller and smaller ink particles that are eventually small enough to be removed by the body's immune cells. Because of this process, multiple laser treatments are required to begin to visually fade a tattoo, even though the process of making the ink particles smaller begins after just the first treatment.
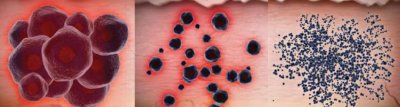
The tattoo ink fragments into smaller and smaller particles with each consecutive laser treatment until finally the ink fragments are small enough to be removed by the body.
Q-Switched YAG Tattoo Removal Laser
The Nd:YAG Q-switched laser is the gold standard laser for safe and effective tattoo removal. The laser has a dual wavelength of 532 nm and 1064 nm which can treat all darker colors and reds. The advantages of the Nd:YAG Q-switched laser include a large spot size, concentrated energy densities, high repetition rates, and greater beam diameter, allowing for rapid, effective treatment of closely clustered and deep tattoos. The 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser has the deepest penetration and thus has the least risk for hypopigmentation (loss of the natural pigment of skin) when used for treatment of black and dark blue ink. It is also considered the ideal choice for tattoo removal in dark-skinned patients, since its longer wavelength caused the least amount of damage to the skin's natural pigment melanin. The 532-nm Nd:YAG laser is the most effective for removal of red, yellow, and orange pigments. Additional wavelengths of 585 nm and 650 nm are available using the polymer dye handpieces which allow treatment of all lighter colors. The Medlite C6 and the related Revlite by Cynasure are the most reliable and proven devices used for tattoo removal. With the R20 protocol, where 4 treatments are performed in the same session, safe and effective tattoo removal has never been faster.

Laser tattoo removal with the Medlite C6 Q-Switched YAG laser. * Individual results may vary.
Q-Switched Ruby Tattoo Removal Laser
The Ruby laser is also used for the removal of black, blue-black, and dark blue pigments. However, mixed results have been reported for removal of green ink and medium blue ink. The ruby laser is not good for removal of red, orange, and pale blue inks. Since this laser's wavelength (694 nm) is absorbed by melanin (the natural pigment of the skin), its use may result in hypopigmentation (loss of the natural pigment of skin).
Q-switched Alexandrite Tattoo Removal Laser
The Q-switched Alexandrite Laser is generally used to remove black, blue, and green pigments. This is not an ideal laser for treatment of red or orange inks. The other issues with this laser is that it is more likely to cause hypopigmentation (loss of the natural pigment of skin) due to the fact that the 755 nm wavelength is absorbed by melanin (the natural pigment of the skin). Transient hypopigmentation, typically lasting three to four months, occurs in about half of patients treated with this type of laser.
Picosure Alexandrite Tattoo Removal Laser
The Picosure laser is a picosecond laser which utilizes the 755 nm wavelength. Although claims have been made that this laser is faster at removal of tattoos than the nanosecond lasers, the experience of many patients has proven otherwise. Two other issues with this lasers are the fact that it does not treat red ink very well and that it is more likely to cause hypopigmentation (loss of the natural pigment of skin) due to the fact that the 755 nm wavelength is absorbed by melanin (the natural pigment of the skin).
R20 Method for Fast Tattoo Removal
The R20 method or R20 protocol is a method of completing four laser tattoo removal treatments in 20-minute intervals all performed during a single 60 minute office visit. In clinical studies, one session of 4 treatments was sufficient to nearly (~ 70%) clear a tattoo of black ink. The passes of the laser are done with 20-minute breaks in between, as opposed to coming in for another office visit weeks later. Four passes in total are completed in one visit with the R20 method, which is often times enough to significantly clear an unwanted tattoo in just one visit.

The R20 method allows fast treatment of tattoos in the least number of session, more than 4 times faster than traditional methods. * Individual results may vary.
The 'R' in R20 stands for repeating or rapid while the '20' stands for the 20 minute wait between each of the 4 treatments. A 20 minute wait period is required because each pass of the laser results in frost like layer, caused by very small nitrogen bubbles on top of the tattoo. Because the laser cannot penetrate through this frost, a 20 minutes waiting period is necessary before the next laser treatment can be performed. Not everyone is a candidate for R20 tattoo removal and the R20 technique works best with dark tattoos as opposed to colored tattoos. There is some additional risk of blistering with the R20 technique.
Risks and Side Effects of Laser Tattoo Removal
Although Q-switched lasers are generally quite safe and effective in tattoo removal, their use is not without occasional adverse effects. The most common adverse effects are:
- Hypopigmentation - lightening of skin
- Hyperpigmentation - darkening of skin
- Darkening of tattoo
- Blistering
- Allergic reaction
- Scarring
Hypopigmentation
The most common side effect of laser tattoo removal is hypopigmentation, or loss of the natural pigment of skin. This risk is higher in dark-skinned patients undergoing treatment with the Ruby or Alexandrite lasers. Hypopigmentation is typically temporary and lasts for two to six months but it can be permanent. The Q-switched Nd:YAG laser is the safest laser for individuals with darker skin color in regards to minimizing hypopigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation or excessive darkening of the skin occurs as a result of increased melanin production in response to laser-generated heat. This effect is usually temporary and the risk of hyperpigmentation depends largely on skin type, with darker-skinned patients being at higher risk. Patients at risk for hyperpigmentation should avoid excessive sun exposure before and after laser tattoo treatments and use sun blocks. Hyperpigmentation can also be treated with lightening creams such as 4% hydroquinone.
Paradoxical Darkening of the Tattoo
Darkening of a tattoo may occur when the composition of the ink is changed by laser treatment. Darkening is often difficult to correct and may require the use of several lasers, including ablative lasers such as Ultrapulse CO2 and/or Erbium:YAG lasers.
Blistering
Blistering can at times occur as a result of laser treatment. Blisters may be avoided by icing or using other skin cooling devices such as the Zimmer.
Allergic Reactions
Tattoo ink may contain metal salts based on mercury, cadmium, chrome, or cobalt. A pre-existing allergic reaction to one of these metals may be exacerbated by laser treatment, resulting in hives or other allergic reaction. Red is the pigment most often associated with allergic reactions, resulting in lumpy, scaly, and itchy areas. Removal of areas of red pigment with the 532-nm Nd:YAG laser can help prevent complications. Allergic reactions can also be treated with steroids.
Scarring
Although uncommon, scarring can occur after any type of laser treatment of the skin, including laser tattoo removal. The risk for scarring is highest on the chest, outer upper arm, and ankle. The risk of scarring is also higher in laser treatment of areas that have been re-tattooed (a second tattoo applied to cover an older tattoo) because of the high density of pigment ink. To minimize the risk of scarring:
- Avoid smoking since the success of removing a tattoo after 10 treatments is reduced by 70% in smokers.
- Wash the treatment site twice a day with mild soap and water. Pat dry with a towel to dry, but don't rub.
- Don't pick any scabs and don't pop any blisters that may occur.
- Keep the tattoo out of the sun, before and after treatments. When in the sun, wear sunscreen that contains zinc or titanium dioxide to block against UVA and UVB rays.
How do I know if I am a good candidate for laser tattoo removal?
The best way to know of course is to come in for a consultation, but if you don't have time for that, the next best thing would be to submit a few photos to us which we can have reviewed by the provider and get back to you with a recommendation.
Contact Us
If you are interested in Laser Tattoo Removal please fill out this Laser Inquiry Form. You will find our staff to be knowledgeable, professional, accommodating, and honest.






